Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
FBrCCA
This script shows how to use FBrCCA from PyntBCI for decoding c-VEP trials. The FBrCCA method uses a template matching classifier where templates are estimated using reconvolution and canonical correlation analysis (CCA). Additionally, FBrCCA uses a filterbank (FB).
The data used in this script come from Thielen et al. (2021), see references [1] and [2].
References
import os
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import seaborn
import pyntbci
seaborn.set_context("paper", font_scale=1.5)
Set the data path
The cell below specifies where the dataset has been downloaded to. Please, make sure it is set correctly according to the specification of your device. If none of the folder structures in the dataset were changed, the cells below should work just as fine.
path = os.path.join(os.path.dirname(pyntbci.__file__)) # path to the dataset
n_subjects = 5
subjects = [f"sub-{1 + i:02d}" for i in range(n_subjects)]
Analyse multiple participants
In this section, we directly apply FBrCCA and compare it to a single-band rCCA using the pass-bands defined in the filterbank.
# Set trial duration
trialtime = 4.2 # limit trials to a certain duration in seconds
n_trials = 100 # limit the number of trials in the dataset
# Set rCCA (see pyntbci.classifiers.rCCA)
event = "duration" # event definition type
encoding_length = 0.3 # length of a transient response in seconds
onset_event = True
# Set folds for chronological cross-validation
n_folds = 5
folds = np.repeat(np.arange(n_folds), int(n_trials / n_folds))
# Set filterbank (see pyntbci.utilities.filterbank)
tmin = 0 # seconds before trial onset that could catch filter artefacts and is cut off after the filterbank
filterbank = [ # passbands with lower and higher cutoffs in Hz
(1.0, 60.0),
(12.0, 60.0),
(30.0, 60.0)]
ftype = "chebyshev1" # filter type
gpass = 3 # maximum attenuation in the passband in dB
gstop = 20 # minimum attenuation in the stopband in dB
n_bands = len(filterbank)
# Loop participants
accuracy_rcca = np.zeros((n_subjects, n_folds, n_bands))
accuracy_fbrcca = np.zeros((n_subjects, n_folds))
for i_subject in range(n_subjects):
subject = subjects[i_subject]
# Load data
fn = os.path.join(path, "data", f"thielen2021_{subject}.npz")
tmp = np.load(fn)
fs = int(tmp["fs"])
X = tmp["X"][:n_trials, :, :int(trialtime * fs)]
y = tmp["y"][:n_trials]
V = tmp["V"]
# Apply filterbank
X = pyntbci.utilities.filterbank(X, filterbank, fs, tmin=tmin, ftype=ftype, gpass=gpass, gstop=gstop)
# Cross-validation
for i_fold in range(n_folds):
# Split data to train and test set
X_trn, y_trn = X[folds != i_fold, :, :, :], y[folds != i_fold]
X_tst, y_tst = X[folds == i_fold, :, :, :], y[folds == i_fold]
# Setup classifier
rcca = pyntbci.classifiers.rCCA(stimulus=V, fs=fs, event=event, encoding_length=encoding_length,
onset_event=onset_event)
gate = pyntbci.gates.AggregateGate("mean")
fbrcca = pyntbci.classifiers.Ensemble(estimator=rcca, gate=gate)
# Train classifier
fbrcca.fit(X_trn, y_trn)
# Apply classifier
yh_tst = fbrcca.predict(X_tst)
# Compute accuracy
accuracy_fbrcca[i_subject, i_fold] = np.mean(yh_tst == y_tst)
# Loop individual pass-bands
for i_band in range(n_bands):
# Setup classifier
rcca = pyntbci.classifiers.rCCA(stimulus=V, fs=fs, event=event, encoding_length=encoding_length,
onset_event=onset_event)
# Train classifier
rcca.fit(X_trn[:, :, :, i_band], y_trn)
# Apply classifier
yh_tst = rcca.predict(X_tst[:, :, :, i_band])
# Compute accuracy
accuracy_rcca[i_subject, i_fold, i_band] = np.mean(yh_tst == y_tst)
# Stack results
accuracy = np.concatenate((accuracy_fbrcca[:, :, np.newaxis], accuracy_rcca), axis=2)
# Plot accuracy
plt.figure(figsize=(15, 4))
for i in range(1 + len(filterbank)):
if i == 0:
label = "FBrCCA"
else:
label = f"rCCA {filterbank[i - 1][0]:>4}-{filterbank[i - 1][1]:>4}"
width = 0.9 / (1 + len(filterbank))
plt.bar(i * width + np.arange(n_subjects), accuracy[:, :, i].mean(axis=1), width,
yerr=accuracy[:, :, i].std(axis=1), label=label)
plt.axhline(1 / V.shape[0], linestyle="--", color="k", alpha=0.5, label="chance")
plt.xticks(width * (len(filterbank) / 2) + np.arange(n_subjects), subjects, rotation=45)
plt.legend(bbox_to_anchor=(1.0, 1.0))
plt.ylabel("accuracy")
plt.title("Decoding performance full dataset")
plt.tight_layout()
# Print accuracy
for i in range(1 + len(filterbank)):
if i == 0:
label = "FBrCCA"
else:
label = f"rCCA {filterbank[i - 1][0]:>4}-{filterbank[i - 1][1]:>4}"
print(f"{label}: {np.mean(accuracy[-1, :, i]):.2f} +/- {np.std(accuracy[-1, :, i]):.2f}")
# plt.show()
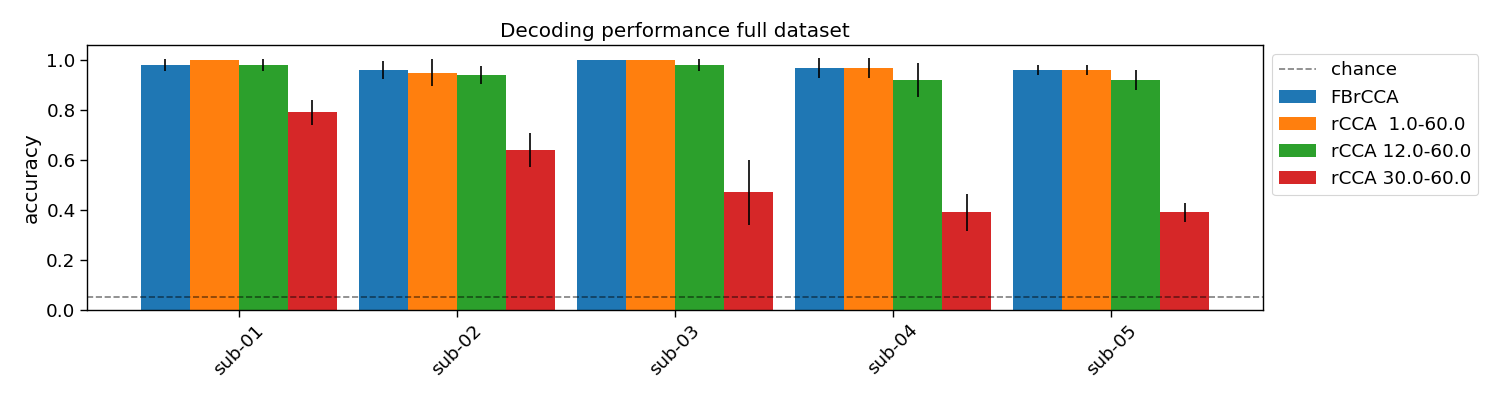
FBrCCA: 0.96 +/- 0.02
rCCA 1.0-60.0: 0.96 +/- 0.02
rCCA 12.0-60.0: 0.92 +/- 0.04
rCCA 30.0-60.0: 0.39 +/- 0.04
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 37.796 seconds)